Can’t decide between Outbound vs Inbound Sales strategies for your business? Both methods have clear advantages. Inbound leads tend to convert at rates up to 14.6%, often coming from prospects who already know they need a solution. Outbound lets you target ideal customers directly, creating high-value deals with proper nurturing. Many B2B companies now use a hybrid approach, combining the two for faster revenue growth and better pipeline coverage.
What are Outbound vs Inbound Sales?
The main difference between Outbound vs Inbound Sales comes down to who takes the first step, and understanding this is key to a successful strategy.
What are Inbound Sales?
Inbound sales happen when prospects come to you first. They may have discovered your brand through SEO, social media, ads, or referrals. They already understand their problem and are actively seeking a solution. Inbound focuses on providing helpful content, answering questions, and guiding buyers naturally toward your product.
Outbound sales work differently; your sales team actively reaches out to potential customers who may not know your brand or even realize they have a problem. You research their pain points and send personalized messages, cold calls, emails, or social media outreach to capture their interest.
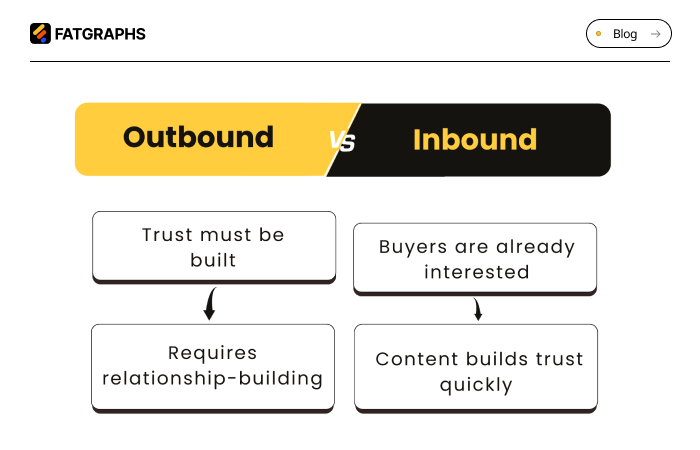
Both approaches move through the sales funnel, but they handle the early stages differently. Inbound builds trust through content and education, while outbound requires persistence, strong communication, and relationship-building.
What are Outbound sales?
Outbound sales involve proactively reaching out to leads who haven’t shown prior interest. This approach remains a cornerstone in B2B sales. In fact, outbound methods generate about 55% of leads, compared to just 27% for inbound in many industries.
Common outbound tactics include cold calling, cold emailing, LinkedIn outreach, social selling, and direct mail. Some may call these “old school,” but they are highly effective when targeting specific decision-makers or niche markets. Outbound gives your team full control over whom you contact, making it ideal for high-value deals.
For example, a SaaS company targeting enterprise IT managers can send personalized LinkedIn messages and follow up with calls to book meetings, instead of waiting for the managers to find them. This approach ensures your team is proactive and pipeline gaps are filled quickly.
Key differences in buyer behavior
B2B buyers behave differently from B2C consumers. Emotions play a huge role in decisions, along with logic and ROI. Many purchases involve multiple stakeholders. For instance, buying enterprise software often requires approval from the CIO, CFO, and CMO. Each leader looks at different factors: system compatibility, cost, and customer engagement features.
Trust is critical, especially in outbound sales, where you initiate contact. Prospects research extensively before committing, and building relationships is essential. Inbound buyers, on the other hand, come to you already interested and tend to trust your content before interacting with your sales team.
For example, a CFO might read a blog on cost-saving software features and become interested in a demo, while the CIO might need a personalized outreach explaining integration options. Understanding this difference is key to designing effective sales strategies.
Comparing Outbound vs Inbound Sales Performance
1- Lead quality and conversion rates
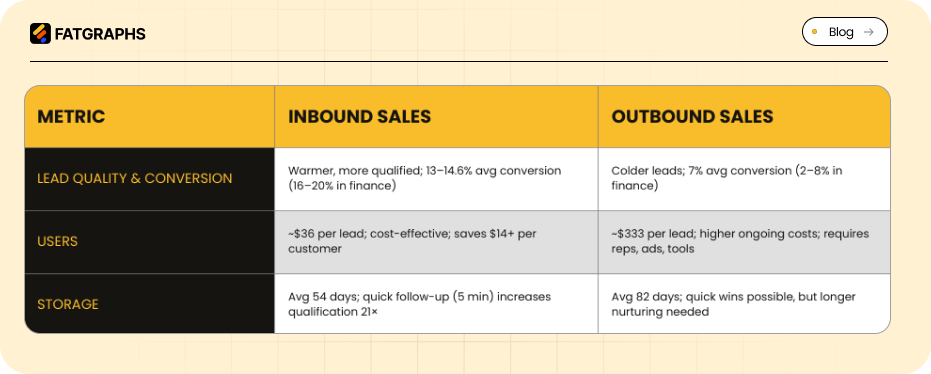
Inbound leads tend to be warmer and more qualified because they actively engage with content. On average, inbound leads convert at about 13-14.6%, while outbound leads convert around 7%. In banking and financial services, inbound conversion can reach 16-20%, while outbound may only convert 2-8%.
This difference shows the power of providing value first. For example, HubSpot found that offering free resources like templates or guides increased lead conversion by nearly 15%, compared to outbound outreach alone.
2- Cost per lead and ROI
Inbound is more cost-effective in the long run. The average inbound lead costs around $36, compared to $333 for outbound leads. Companies focusing on inbound can save over $14 per new customer and generate three times more leads for the same budget.
Outbound requires more continuous investment, including sales reps’ time, ad spend, and tools. For instance, a company targeting enterprise HR managers might spend hundreds of dollars per lead on LinkedIn ads and manual outreach. Despite the higher cost, outbound can generate highly targeted opportunities.
3- Sales cycle length and speed to revenue
Outbound methods can book qualified meetings in days or weeks, giving quick initial results. However, inbound deals often close faster overall. Inbound sales cycles average 54 days, while outbound cycles can take 82 days.
Fast follow-up is crucial. Teams that respond to inbound leads within five minutes are 21 times more likely to qualify them than those waiting 30 minutes. This shows that even inbound leads need timely engagement to accelerate revenue.
Modern Outbound vs Inbound Sales Strategies
Inbound: content, SEO, and fast follow-up
Successful inbound strategies focus on content that answers buyers’ questions directly. Using SEO ensures your content is discoverable, while lead magnets like ebooks, checklists, or webinars capture interest. Lead scoring helps prioritize prospects based on engagement and demographics.
For example, a marketing software company might publish a blog on email campaign best practices, capture leads through a free checklist download, and follow up within minutes with a demo invitation. Quick, relevant responses make the inbound process highly effective.
Outbound: multichannel outreach and personalization
Modern outbound prioritizes precision over volume. Omnichannel sequences combining email, phone, LinkedIn, and direct mail increase ROI by 24% compared to single-channel efforts. Personalized, context-aware messaging tailored to the buyer’s role and stage is essential.
A case in point: a B2B cybersecurity firm targeting IT directors can send a LinkedIn message referencing a recent security incident, follow up with a personalized email, then a call, significantly increasing engagement compared to generic cold emails.
How inbound and outbound strategies have risen in 2026
AI is now a major factor in both approaches. AI-powered prospecting saves 4-7 hours per week per salesperson, allowing more time for relationship-building. High-performing teams use hybrid human-AI models: AI handles research, data analysis, and first-touch personalization, while humans focus on closing and nurturing relationships.
For example, an AI system can prioritize leads showing intent signals, while the sales rep focuses on tailoring calls and emails, increasing efficiency and reducing wasted effort.
Why a hybrid strategy drives faster revenue
Combining the strengths of both approaches
Inbound and outbound work best together. Outbound pushes information to prospects while inbound attracts interested customers naturally. This combination ensures consistent lead flow and higher pipeline coverage.
SuperAGI, a tech company, boosted meetings by 40% using a hybrid model, while companies integrating AI into both Outbound vs Inbound Sales saw 15% higher sales efficiency and 10% lower costs. McKinsey research predicts hybrid models will drive 22% higher revenue growth by 2026.
How hybrid models improve pipeline coverage
Hybrid models engage prospects throughout the buyer journey, from awareness to decision. By combining inbound signals with outbound targeting, teams stay agile, adapt to market changes, and maintain a healthy pipeline.
Intent data, lead scoring, and analytics allow sales reps to focus on the highest-value prospects while nurturing cold leads. This ensures no opportunity is missed, and pipelines remain robust.
Examples of hybrid success in action
- SuperAGI: Combined inbound webinars with outbound LinkedIn outreach, increasing qualified meetings by 40%.
- Enterprise SaaS company: Used AI to personalize outbound emails and optimize inbound content, boosting sales efficiency by 15% and reducing costs by 10%.
- McKinsey study: Hybrid sales models saw up to 22% higher revenue growth, proving the approach scales across industries.
Conclusion
Outbound vs Inbound Sales: each offers unique benefits. Inbound provides higher conversion rates and lower costs, ideal for businesses with longer sales cycles and content-driven strategies. Outbound excels at targeting specific accounts, filling pipeline gaps quickly, and reaching high-value prospects.
The best strategy is a hybrid approach. Companies using both methods see up to 38% faster revenue growth, consistent pipeline coverage, and better adaptation to changing market conditions. AI integration further enhances efficiency, personalization, and relationship-building.
Instead of choosing one over the other, analyze your pipeline gaps and business goals. Use inbound to attract interested leads and outbound to proactively target ideal accounts. Together, they magnify each other’s strengths, delivering faster, more sustainable revenue growth.
FAQs
Q1. Which approach is more cost-effective, inbound or outbound sales?
Inbound is generally cheaper, costing around $36 per lead versus $333 for outbound. Businesses save over $14 per new customer when using inbound strategies.
Q2. How do conversion rates compare?
Inbound leads convert at 13-14.6%, while outbound leads convert around 7%. In some sectors, inbound conversion can reach 16-20%, compared to outbound’s 2-8%.
Q3. Which generates faster results?
Outbound can book meetings within days or weeks, but inbound deals often close faster overall, with sales cycles averaging 54 days versus 82 for outbound.
Q4. How has AI impacted modern sales?
AI saves 4-7 hours weekly per salesperson, handling research and first-touch personalization, allowing reps to focus on high-value relationship building.
Q5. Should I focus on inbound, outbound, or both?
A hybrid approach yields the best results, improving pipeline coverage, adaptability, and revenue growth. Companies using integrated strategies see up to 38% higher revenue growth.

 Book Call with Haroon
Book Call with Haroon

